Introduction
In the context of growing global concerns about climate change and environmental degradation, countries around the world are striving to find a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability. Bangladesh, a nation highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, faces significant challenges in managing the environmental consequences of rapid industrial and microenterprise growth. The country’s microenterprise sector plays a crucial role in its economy, contributing significantly to employment and GDP. However, the sector’s expansion often comes at the cost of environmental degradation, inefficient resource use, and increased vulnerability to climate shocks. This global and national context underscores the urgent need for projects that foster sustainable, climate-resilient growth in Bangladesh’s microenterprise sector.
The Sustainable Microenterprise and Resilient Transformation (SMART) project is a key initiative aimed at driving resource-efficient and climate-resilient green growth in the microenterprise (ME) sector of Bangladesh. Launched with a significant financial contribution from the World Bank and additional support from the Palli Karma-Sahayak Foundation (PKSF), this project seeks to address the environmental challenges posed by the rapid expansion of microenterprises.
The SMART project focuses on promoting Resource-Efficient and Cleaner Production (RECP) practices among MEs, aiming to improve environmental sustainability, enhance productivity, and build climate resilience. SMART project comprises three major components: enabling capacity and systems for green growth, providing access to finance, and improving project management and knowledge dissemination.
The project focuses on providing support to microenterprises operating in agribusiness, manufacturing, and service sectors, with a specific emphasis on environmentally stressed areas susceptible to climate change and natural disasters. Additionally, the project aims to encourage development of environment-friendly businesses and the adoption of operational safety standards within microenterprises. The SMART project places significant emphasis on the need for capacity building, technology adoption, knowledge sharing, and behavioral change among microenterprises. This multifaceted approach ensures the promotion of green growth solutions that are both sustainable and beneficial the environment.
By integrating green growth approaches, enhancing capacity-building initiatives, and facilitating access to finance, SMART seeks to create a robust and sustainable ME sector in Bangladesh, supporting the country’s long-term development goals while addressing climate vulnerabilities.
Objective: The objective of the SMART project is to increase resource-efficient and resilient green growth of microenterprises, encapsulating three core concepts.
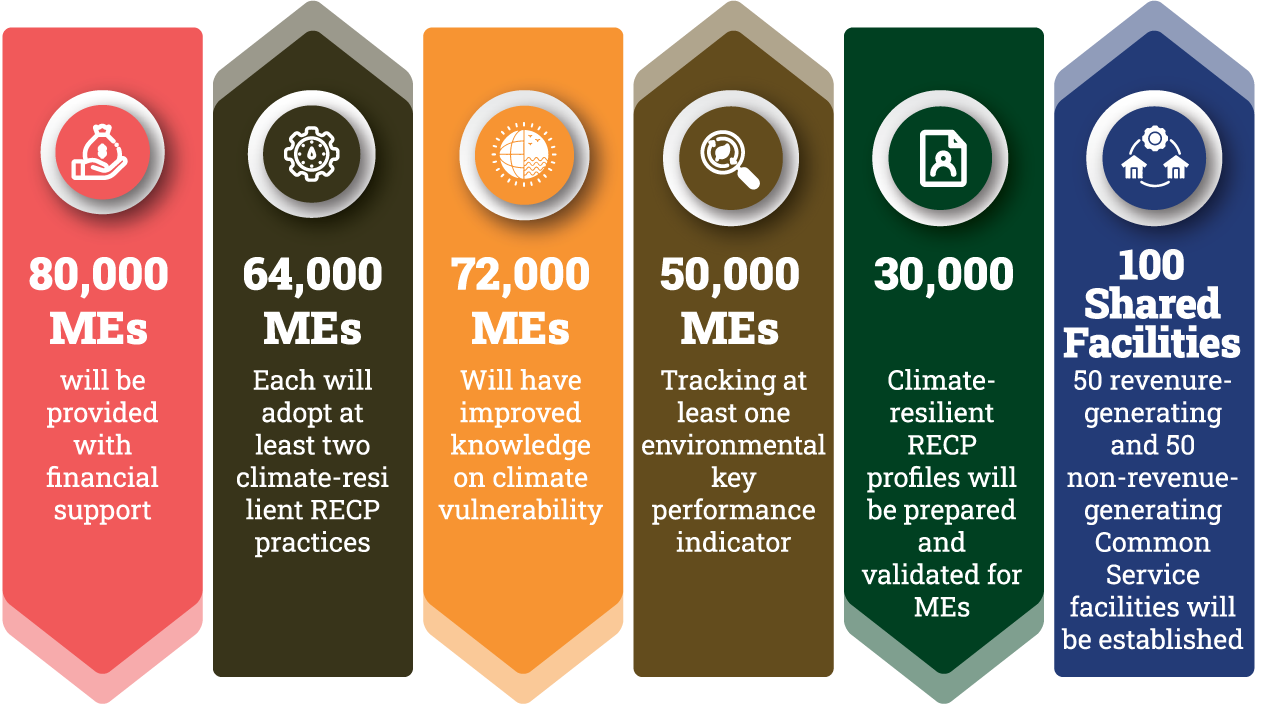
Targeted microenterprises: 80,000 microenterprises in agribusiness, manufacturing and service
Targeted Area: All over Bangladesh with a special focus on climate-vulnerable areas

Budget
The total budget of the project is USD 300 million, of which the World Bank and PKSF’s contribution is USD 250 million and USD 50 million respectively.
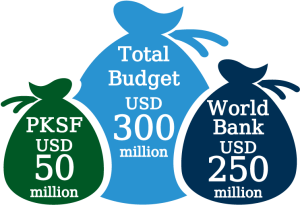
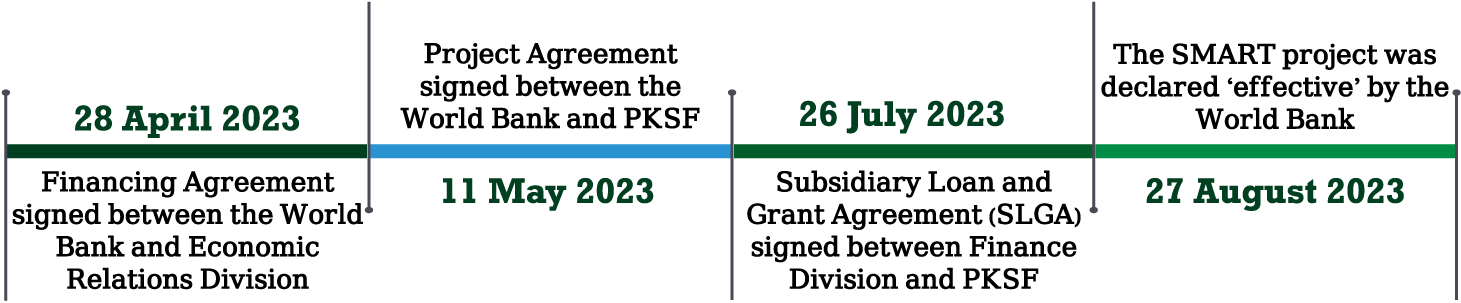
Key timeline
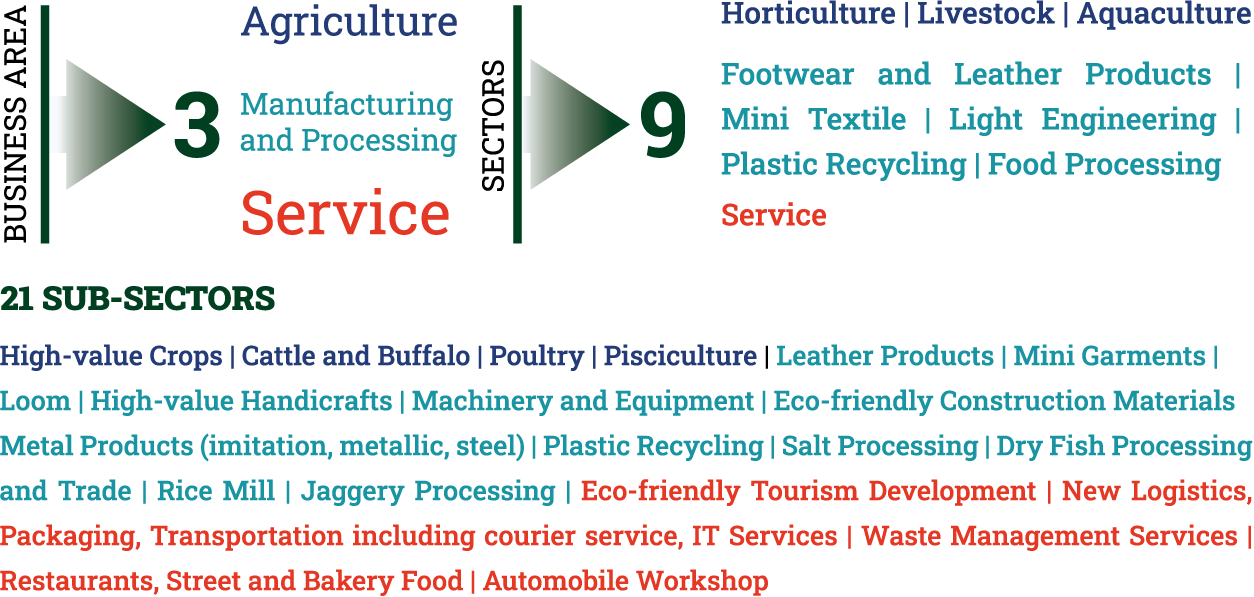
Scope
The project will operate nationwide, with a special emphasis on areas particularly vulnerable to climate change-related shocks. The interventions are structured across 3 business areas, 9 sectors, and 21 sub-sectors.
Approach
The SMART project focuses on transforming the ME sector into a more dynamic, lower-polluting, resource-efficient, and climate-resilient sector. It will support measures that enhance climate resilience by promoting RECP knowledge, technology, and business processes.
Microenterprises at the center: The project has been designed with microenterprises at its heart, ensuring that all services, resources, and support are directed toward empowering them. This core focus guarantees that microenterprises receive the necessary assistance to drive sustainable growth and resilience.
Sub-project-based implementation: The SMART project will be implemented through PKSF’s Partner Organizations (POs) at the field level. Each PO will implement the project under individual sub-projects, spanning 21 selected sub-sectors. Additionally, the project will emphasize a cluster-based approach, ensuring that interventions are tailored to the specific needs and challenges of groups of microenterprises operating in the same geographic or industrial clusters.
Promoting Climate-Resilient RECP Practices and Tracking Environmental Key Performance Indicators: The project focuses on Resource-Efficient and Cleaner Production (RECP) technologies, enabling MEs to anticipate and adapt to the challenges of climate change. It will also maintain a robust monitoring mechanism for tracking the environmental performance indicators in terms of air quality, water quality, waste management, electricity consumption, etc.
Fields of Support: The project prioritizes MEs operating in agribusiness, manufacturing, and services, focusing on regions vulnerable to environmental stress and natural disasters.
Building Capacity and Encouraging Innovation: The SMART project emphasizes on the need for knowledge sharing, technology adoption, and fostering a shift towards environmentally responsible practices within MEs. This multifaceted approach ensures long-term sustainability and positive environmental impacts.
Maximizing Impacts: SMART strategically prioritizes interventions based on key principles such as business clusters, pollution reduction, ecosystem protection, and the potential for wider replication and scaling.
The project will target both formal and informal MEs in specific sectors with high environmental improvement potential. Women entrepreneurs will remain in focus.
Expected Results
The SMART project will contribute to Bangladesh’s long-term environmental sustainability, and it’s aligned with the 8th Five Year Plan, the Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC), and the National Adaptation Plan (NAP), 2022, which are the country’s roadmaps to promoting economic growth and poverty reduction and paying special attention to MEs and environmental sustainability.
The project’s long-term impact is to transform the ME sector into a more dynamic, lower-polluting, resource-efficient, and climate-resilient ME sector.